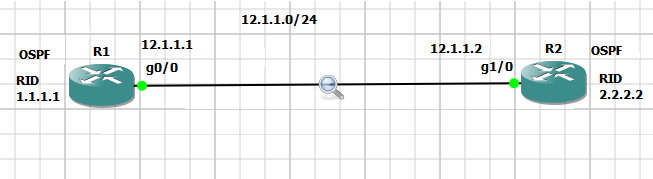
OSPF stands for open shortest path first.
1. It is an open standard protocol. Open standard means that It supports two different vendors like – Cisco, Huawei, juniper, etc.
3. It is a link-state routing protocol. link-state means In OSPF routers do not send periodically update, only send update whenever changes will occur in the topology and that information will be sent partial means in which changes occurred.
And link state routing protocol whenever share own prefix information that time it also shares own subnet mask information with its neighbors.
4. It is an IGP protocol. IGP means it works within AS.
5. OSPF uses the SPF algorithm or you can say the Dijkstra algorithm for best path selection.
6. Supports unlimited hop count which means no limitation of hop count in OSPF.
7. OSPF uses protocol no – 89
8. It is a layer-3 protocol
9. AD value is = 110
10. Hello and dead interval timer = 10 sec, 40 sec (by default).
Broadcast and point to point = 10sec, 40sec.
Non- broadcast and point to multipoint = 30sec, 120sec.
11. Metric = Cost.
By default reference bandwidth = 100
Ethernet cost = 10
Fast Ethernet cost = 1
Giga ethernet cost = 1
Serial link cost = 64
Note – OSPF does not consider decimal values while calculating cost.
12. It is a classless routing protocol; classless means whenever it will share prefix information/ Network information with its neighbors that time it shares subnet mask information with the neighbors.
13. OSPF uses two multicast addresses-
224.0.0.5 (All routers listen)
224.0.0.6 (DR routers listen)
In OSPF hello packets are sent through multicast address 224.0.0.0.5
Note – In static case may be sent = 224.0.0.6
14. In OSPF must have one area called area 0 and all the areas must be connected to area 0.
15. Supports authentication.
Type 0 – Null authentication
Type 1 – Plain text authentication
Type2 – MD5 authentication
16. Incremental and triggered updates.
17. Introduce the concept of areas to ease management & control traffic.
18. OSPF provides a Hierarchical Network design with multiple different areas.
19. Routers send only changes in updates and not the entire routing table in periodic updates.
20. By default auto-summary is disabled
21. By default maximum path = 4 (Maximum up to 16).
How to calculate OSPF cost = ( In serial link )
# show ip ospf neighbor
2. Database table-
The database table contains information about the entire view of the topology with respect to each other (Complete information on the same area but no information on the other area).
#show ip ospf database
3: Routing table –
Routing table contains information about the best path calculated by SPF algorithm in data base table.
#show ip route ospf
Points to be noted –
In ospf each router makes own database table and in that database table are LSA and in that LSA router Keeps Links information.
For an instance – R1 router.
Types of the packet in OSPF:
Type1 :hello
Type2 : DBD database description
Type3: LSR Link state request
Type4: LSU Link state update (retransmission time out 5sec)
Type5: LS Ack link state acknowledge
Hello:-
1. Hello packets are used to establish & maintain Neighbor-ship.
2. Hello packets are used to discover neighbor-ship.
3. Keep alive.
4. Periodically send after every 10sec/30sec (Brod, P2P/Non-Broadcast).
5. Dead timer 40sec/120sec (Brod, P2P/Non-Broadcast).
6. Hello messages are sent through multicast address – 224.0.0.5.
7. In static neighbor-ship hello messages/packets are sent unicast.
Hello packets content:-
1. OSPF version
2. Message type
3. Packet length
4. Router-id
5. Area-id
6. Checksum value
7. Authentication type
8. Authentication data
9. Subnet mask
10. Hello & Dead interval timer
11. Priority
12. DR & BDR IP address
13. Stub area flag.
Type2 : DBD database description.
1. In this packet routers only exchange empty DBDs packets with their own sequence number to neighbors.
2. Also routers share MTU size in this packet. (MTU Size must be the same in a packet of the router’s interface).
3. Master/ Slave is elected. And that router will become the master router whose router-id will be higher than the other and the master router will start the exchange of information and other routers (Slave) will give a response to the master.
Type-3– Link state Request (LSR):-
In this state will request to its neighbors that I am having some LSA header and I need complete information about that ok let me check in my database table, and Vice versa.
Type-4 – Link state update (LSU):-
In this packet/message router will share updates about its own links information to neighbors.
Type -5- link state acknowledgment (LSack)
Then routers will give each other an acknowledgment message.
Types of OSPF states
1. Downstate
2. Init state
3. 2-way state
4. Ex-start state
5. Exchange state
6. Loading state
7. Full state